Your Complete Guide | What is Harmonized System (HS) Codes
Do you work with the import and export of goods across borders? Understanding HS codes is crucial for this trade. So, What is the Harmonized System (HS) Code?
At first glance, it seems like some random numbers, but these codes are crucial in facilitating international trade. They are considerable assistance with shipping and dealing with local regulations. So, in this blog, we will learn everything you should know about HS Code and its applications.
What is the HS code?
Products are classified and identified for customs reasons using the Harmonized System (HS) Codes, also known simply as HS Codes. The World Customs Organization created the International Trade Code (HS code), which is now used all over the world.
Over 200 countries and economies use this method to compile statistics on international trade and Customs charges. More than 98% of all goods traded internationally are categorized using the HS.
A sequence of numbers, these codes identify specific products according to their qualities, ingredients, or intended purpose. The HS Code was developed so countries worldwide may use the same language to classify things for international trade.
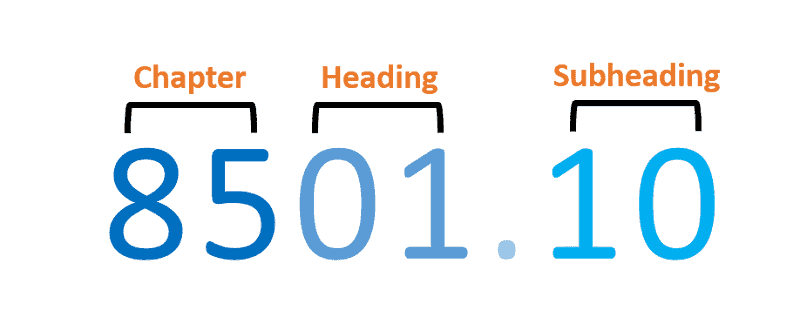
Structure of HS codes
The Harmonized System (HS) code structure is a detailed and extensive system for categorizing goods for international trade.
These codes are six digits long worldwide, with certain countries adding them for even more granular classifications. A unique HS code is assigned to each one to identify and categorize commodities efficiently.
The code is broken into discrete sections representing distinct product types, from primary inputs to final outputs. The first two digits designate the chapter, which broadly categorizes goods into categories with comparable purposes or characteristics.
The following two numbers denote headings that refine the classification based on material composition or application criteria. The subsequent subheadings provide a more granular breakdown down to the four-digit level.
Beyond this point, countries can add national subheadings with additional digits inside their tariff schedules to attain maximum precision.
Let’s use an example to make this more transparent.
Examples include “01” for live animals and “02” for cooked meat and offal. As we progress, additional digits in the code structure reveal more specific information about the product type or its constituent parts.
For instance, the second and third digits of the HS code for beef specify whether the product is fresh or chilled (0201) or frozen (0202), respectively. This structured method ensures international harmony by standardizing trade document language and simplifying precise tariff calculations for imported and exported goods worldwide.
Therefore, businesses gain from the streamlined customs processes and improved visibility into international trade made possible by the HS codes.
Here is a video demonstration
For More Details, you can visit WCO trade tools
How Do the HS Codes work?

By standardizing the language used by customs officials and merchants, HS codes serve a significant role in making international trade more efficient. A product’s type, composition, function, or purpose determines which HS Code it should be assigned to.
Additional numbers may be added to the end of these initial six to denote more specific subcategories. This thorough approach ensures that every item traded globally is properly categorized based on its features. With proper use of the HS Codes, countries can precisely monitor imports and exports and impose the necessary levies and taxes.
Also, governments can measure the products they are importing and exporting, which helps them to take proper action for the following years.
What is the HS code for customs?
The Harmonized System Code, or HS code for short, is an essential part of international trade since it provides a consistent method of categorizing products.
Six digits in this alphanumeric code are utilized by customs agencies worldwide. Customs officials rely heavily on the “HS code” since it helps them quickly and reliably identify products and assign appropriate charges and taxes.
With millions of products handled internationally every year, this coding scheme facilitates open lines of communication between customs agencies worldwide.
What is the HS code on Commercial Invoice?
The HS code (Harmonized System code) is the “heart” of a commercial invoice in international trade. The item description lets the customs and delivery personnel know what to expect from the shipment. Therefore, it is crucial that the correct HS code appears on the invoice.
Here’s how you typically include the HS code on a commercial invoice:
- Description of Goods: Give a detailed description of the items being shipped in the invoice’s “description of goods” section. Specify the product’s name, features, and quantity.
- HS Code: Include the appropriate HS code next to each product description. There are six digits in this code, although some countries utilize more granular categories and hence have their own unique coding systems. Verify that the HS code truly represents your product.
- Country of Origin: Include the nation of origin information for each product. This information is critical for setting import taxes and negotiating trade pacts.
- Value of Goods: Don’t forget to add the monetary amount of each item on the invoice. This is used for determining tariffs and taxes at customs.
- Total Invoice Value: Include all product prices and shipping costs to get the total invoice amount.
NOTE: If you hire an expert freight forwarder, they will complete all of the above tasks.
2022 updates to the HS codes
Every five years, the World Customs Organization (WCO) updates its HS code system to reflect the latest developments in international trade.
The World Customs Organization (WCO) announced the 7th edition of the HS in January 2022. This edition included some minor changes to the HS code requirements.
The rate at which countries implement these upgrades varies. The EU, however, and other major trading blocs swiftly adopted the new rules on January 1, 2022.
Your items must be categorized appropriately and by each country’s customs regulations along your trade route before you can begin exporting or importing them. Legal and business papers need to incorporate the correct HS codes.
The importance of HS codes in international trade

Facilitating Global Commerce
HS codes define goods and commodities by their qualities to streamline customs and ensure worldwide commerce. HS codes help governments unify import/export data and streamline cross-border transactions by precisely categorizing products according to international standards.
Ensuring Consistency and Standardization
The uniformity they bring to international commerce documents is why HS codes are so important. Uniformity is accomplished across areas and markets thanks to these standardized classification codes by 200 participating countries.
This facilitates precise calculation of tariffs, levies, taxes, and other trade-related expenses, easing information sharing between trading partners. Regardless of language hurdles or differences in national rules, HS codes aid in accurately identifying goods by including details such as materials used or production methods employed within the code structure.
Enhancing Customs Efficiency
The timely passage of international trade through borders is essential in reducing congestion generated by inspection procedures. By allowing for automated cargo clearance systems at ports worldwide, HS codes significantly improve customs efficiency.
Authorities can rapidly analyze risk levels connected with certain commodities when shipments are assigned a code that precisely correlates with their product description. Therefore, valuable time is conserved.
Promoting Transparency and Fairness
HS codes help make international trade more open and equitable. They lay out precise rules for categorizing goods consistently across different regions and legal systems. Therefore, during cross-border trade, merchants from other nations can use these standardized categories to learn with certainty which tariff regime applies to their commodities.
This eliminates any room for debate or confusion over the classification judgments various countries make when importing or exporting goods.
Enabling Accurate Trade Statistics
These codes are essential for assuring uniformity and clarity in recording and evaluating trade data, given the wide variety of products traded worldwide daily. Governments can accurately track the items entering and leaving their country by giving unique HS codes to each import and export.
Using this information as a starting point, policymakers can craft tariffs, import/export quotas, economic plans, and resource allocations that are more likely to succeed.
Aside from being a valuable tool for strategic decision-making worldwide, trade statistics obtained from HS code-based reporting enable organizations to identify market trends and assess possible growth prospects precisely.
Consequences of improper HS code use
Misuse of HS codes can have severe ramifications for international trade businesses. Worldwide customs officials use the Harmonized System Code (HS code) to classify imported and exported commodities.
It is appropriately used to ensure precise tariff calculation, proper documentation, and efficient clearing operations. However, misusing HS codes might have serious consequences.
Initial misclassification can lead to improper duty payments, hurting a company’s bottom line. Customs audits may interrupt supply chains and postpone cargo release if HS codes are not followed.
If fraud or evasion is purposeful, using the wrong codes might result in fines or criminal charges.
Using erroneous HS codes reduces the accuracy and reliability of global trade statistics, which are essential for national and international policymaking.
To circumvent these problems, cross-border traders must use HS codes correctly.
FAQ
Where Can I Find the HS Code on my goods?
A little observation and investigation will reveal the answer. First, check your product for marks or labels that may indicate its classification code. Labels are frequently on the packaging or the object itself. Look for labels, tags, or engraved numbers to determine its origin and category. Invoices and shipping paperwork commonly list the product’s HS Code. If these efforts fail, try official government websites for customs regulations and trade statistics.
HS and HTS codes: What’s the difference?
Products are classified according to their type, composition, or function using the World Customs Organization’s (WCO) defined six-digit HS code. It offers a common language for cross-border product categorization.
The HTS code, on the other hand, is a more specialized variant of the HS code used by U.S. Customs and Border Protection for tariff collection.
Finer product differentiation within each HS classification group is made possible by the additional four digits in an HTS code. Both systems are identical in structure and functioning, but they are used for different objectives in international business transactions.
Final Words
If you are with us so far, now you have a clear understanding of what HS Codes are. These are very important in the international trade. Therefore, if you are new in this world, you should know details about these codes otherwise, you can find yourself in serious trouble for any misunderstanding, or in the worst case, scammers can take advantage of your short learning.
At Winsky Freight, we are experts in international trading and can help you include the HS code as per the industry standard on your packages. If you want to know more, feel free to contact us.




Leave A Comment